Large Networks: 5-4-3 rule
A network is also limited in its maximum size, when Repeaters and/or
hubs are used to extend a Thin Ethernet (10base2) or
Twisted Pair Ethernet (10baseT/UTP) network, on large configurations, a
Switch may become necessary to optimize network utilisation..
On Thin-Ethernet, the rules are:
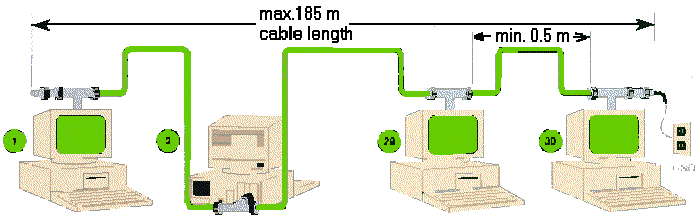
- minimum 0.5 m between T-connectors
- maximum 185 m cable length
- maximum of 30 nodes (i.e.
connections)
An cable can be extended by installing Repeaters, which amplify the signal:
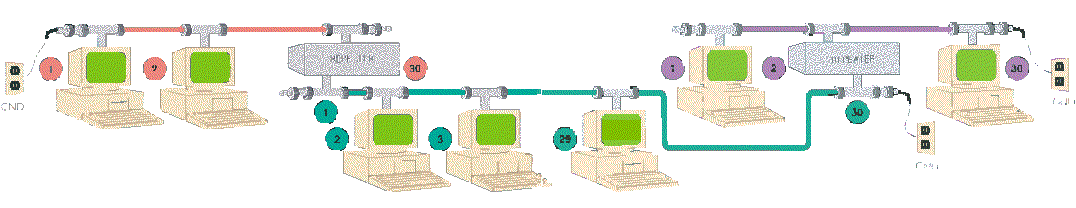
A Repeater counts on each segment as a node and can be connected at ANY location in the Thin-Ethernet cable.
However, if a network needs more than 2 repeater:
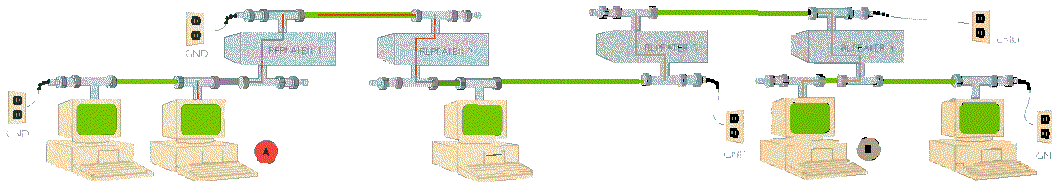
the following limitations apply:
When an Ethernet signal travels from its source to destination station, it can travel
through:
- maximum of 5 segments
- maximum of 4 Repeaters/hubs
- maximum of 3 populated segments
(Populated segments have more than 2 nodes connected, un-populated segments have only a
node at each end, so a 10baseT-segments is a non-populated segment).
And for this discussion, a 10BaseT-Hub is like a repeater and a 10baseT cable can be
treated as a cable 10base2-cable with just 2 systems on it.
There can be more repeaters/hubs in the complete network, and an Ethernet signal can
pass-by more than 4 Repeaters/hubs, as long it does not have to go THROUGH more than 4
Repeaters/hubs.
If these rules are violated, the network becomes unreliable.